top of page
Conference / Symposium Proceedings and Presentations
Strategic Utilization of Dispatchable Loads and Nodal Reserves for Improved Reserve Deliverability - Link
6th International Conference on Electrical Information and Communication Technology
Joyonta Das Joy*,Samin Salsabil, Abtahi Reza ,Nahiyan Bin Noor
In recent years, it has become increasingly clear
that simply having sufficient capacity to meet demand is not
adequate. Ensuring the deliverability of reserves in contingency
scenarios is a significant challenge, further complicated by rising
uncertainties and the integration of Distributed Energy Resources
(DERs) into the system. This research introduces a novel
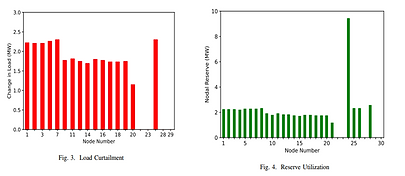
Flexi-Reserve algorithm for detecting deliverability issues under contingency conditions and provides a comparative analysis between dispatchable loads and the availability of operating reserves within the network. Our methodology addresses this challenge by sequentially tackling dispatchable loads, only invoking the operating reserve when conventional sources cannot deliver during a contingency. Our findings indicate that, in a given system, certain nodes can deliver reserve with less need for flexibility, while adhering to operational constraints, thus reducing costs by approximately 40-60%. This study aids in pinpointing optimal nodes for reserves, requiring minimal adjustments or costs, and in identifying areas to avoid, where ensuring flexibility does not necessarily ensure the deliverability of reserves or may lead to elevated costs.

Towards Carbon-Neutral Healthcare Facilities: Design and Evaluation of a Renewable Energy Microgrid-Link
10th IEEE International Conference on Power Systems (ICPS)
Joyonta Das Joy*,Samin Salsabil, Abtahi Reza, Nahiyan Bin Noor
The United Nations (UN) Sustainable Development
Goals (SDGs) demand clean and reliable energy delivery. Here,
we present a comprehensive study focusing on the design,
analysis, and social impact assessment of a microgrid system
tailored for a hospital. The microgrid is designed to support both
grid-connected and islanded operation modes, incorporating PV
panels, wind turbines, combined heat and power (CHP) systems,
and energy storage. In this case study, our objective was to
ensure an uninterrupted power supply during grid blackouts,
achieving a minimum of 75% electricity demand coverage for at
least 5 consecutive days. A detailed cost analysis is conducted,
considering alternative design configurations and the influence
of discount rates on the economic feasibility of the system. To
promote environmental sustainability, a constraint is imposed
on carbon emissions, aiming to keep them below 50% of the
grid emissions. Additionally, a comprehensive social impact
assessment is performed to evaluate the effects of the proposed
microgrid project on various stakeholders in the surrounding
area. The integrated approach of renewable energy integration,
cost analysis, environmental constraints, and social impact assessment contributes to a holistic evaluation, enabling the successful implementation of microgrid systems in similar contexts.

*Presenting/corresponding Author
bottom of page
